Lesson 5b: Decongest the Nose
Decongest the Nose
- Objective:
- To alleviate nasal congestion through controlled breath-holding techniques.
- Directions:
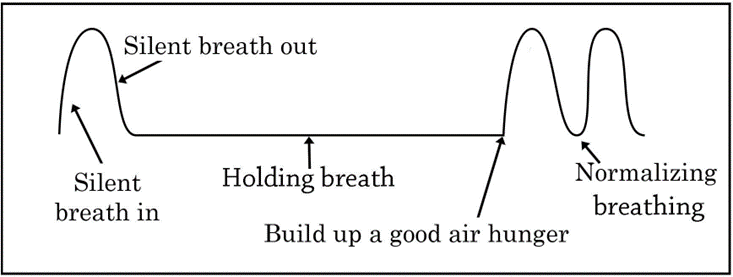
- Sit upright on a straight-backed chair.
- Take a small, light breath in and out through your nose (or the corner of your mouth if nose breathing is not possible).
- After exhaling, pinch your nose and hold your breath, nodding your head or rocking your body until a strong need for air is felt.
- Release your nose and breathe gently in and out through it, avoiding deep breaths.
- Repeat until nasal breathing is eased, potentially practicing up to five times.
- Notes:
- Not suitable during pregnancy or for those with serious medical conditions.
- Regular practice can normalize breathing and improve nasal congestion over time.
- Use of a nasal dilator during rest and exercise may be beneficial.
Exercise #15: Exhale to Improve Diaphragm Function
- Objective:
- To enhance diaphragm functionality, providing postural support and emotional regulation.
- Context:
- The diaphragm, located at the base of the ribs, plays a critical role in breathing, posture, mood regulation, and emotional stability.
- Directions:
- Specific instructions for this exercise are not detailed in the provided text. Refer to additional resources or chapters for guidance.
General Guidelines:
- Practice the nasal unblocking exercise as often as necessary.
- If mouth breathing due to nasal congestion, focus on switching back to nasal breathing.
- For children, additional training videos by Patrick McKeown are available on YouTube.
Safety and Suitability:
- These exercises are suitable for both adults and children, with adaptability for individual needs and conditions.
- Always consider personal health conditions and consult a professional if needed.
This section of exercises provides effective techniques for managing nasal congestion and improving diaphragm function, emphasizing the importance of regular practice and the transition from mouth to nasal breathing for overall respiratory health.
